Anti-Geometry
Anti-Geometry is suspension geometry that is intended to reduce the dive or squat of the car. Anti-geometry includes anti-dive and anti-squat (as well as anti-lift which will not be covered as it is not applicable). Wheel loading remains the same regardless of anti-geometry because the total longitudinal load transfer under acceleration or braking is a function of wheelbase, forces and center of gravity height. Anti-geometry changes amount of load going through the springs and the pitch of the car. Thus, it is largely used for aero benefits.
Side View Swing Arms[edit | edit source]
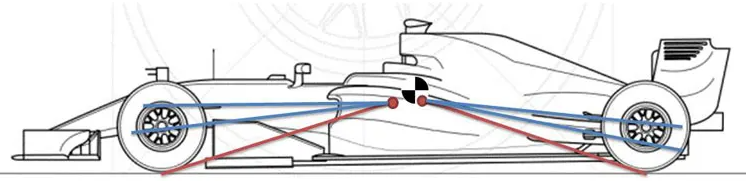
To determine anti-geometry, a side view swing arm must be generated. Draw a line from the 2 mounting points of each front control arm rearward until they touch. Then, draw a line from the 2 mounting points of each rear control arm forwards until they touch. These 2 points are called instant centers. From each instant center, draw a line to its respective wheel's contact patch. This line is the Side View Swing Arm (SVSA).
Anti-Squat[edit | edit source]
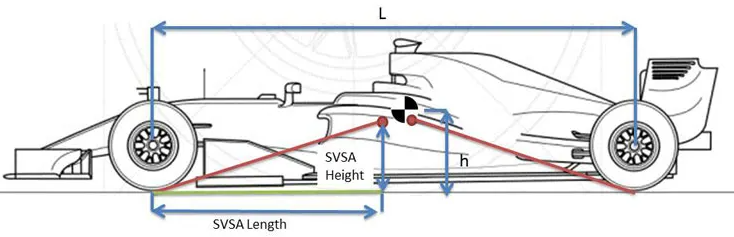
Anti-squat limits the compression of the rear suspension under acceleration. Anti-squat is expressed as a percentage. 100% anti squat represents no rear suspension compression under acceleration. % Anti Squat is calculated using:
Where:
- SVSAheight is the height of the rear instant center from the ground
- SVSAheight is the rear Side View Swing Arm horizontal length
- h is the height of the center of gravity
- L is the wheelbase length
Anti-Dive[edit | edit source]
Anti-dive limits the compression of the front suspension under braking. Anti-dive is expressed as a percentage. 100% anti dive represents no front suspension compression under braking. % Anti Dive is calculated using:
Where:
- SVSAheight is the height of the front instant center from the ground
- SVSAheight is the front Side View Swing Arm horizontal length
- h is the height of the center of gravity
- L is the wheelbase length
- %FrontBraking is the percentage of braking done by the front brake, also known as the brake bias.